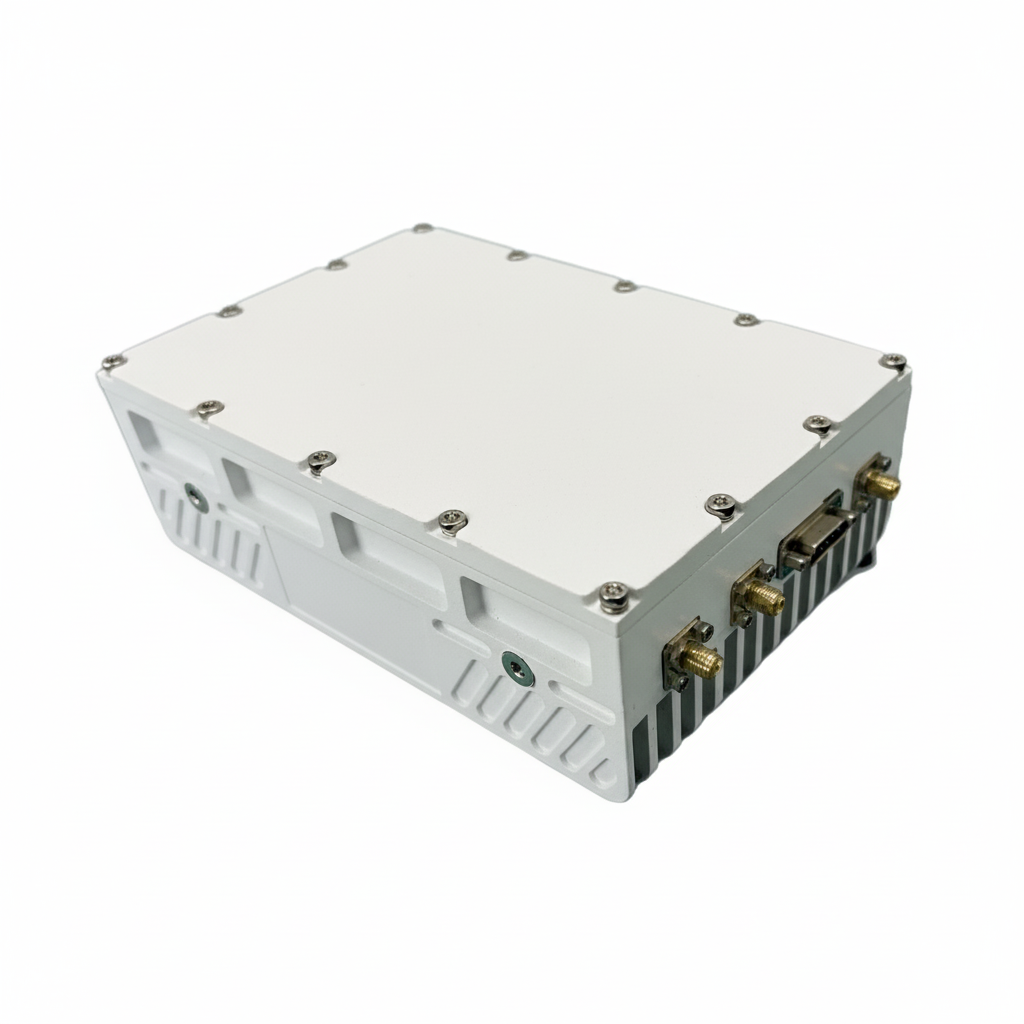
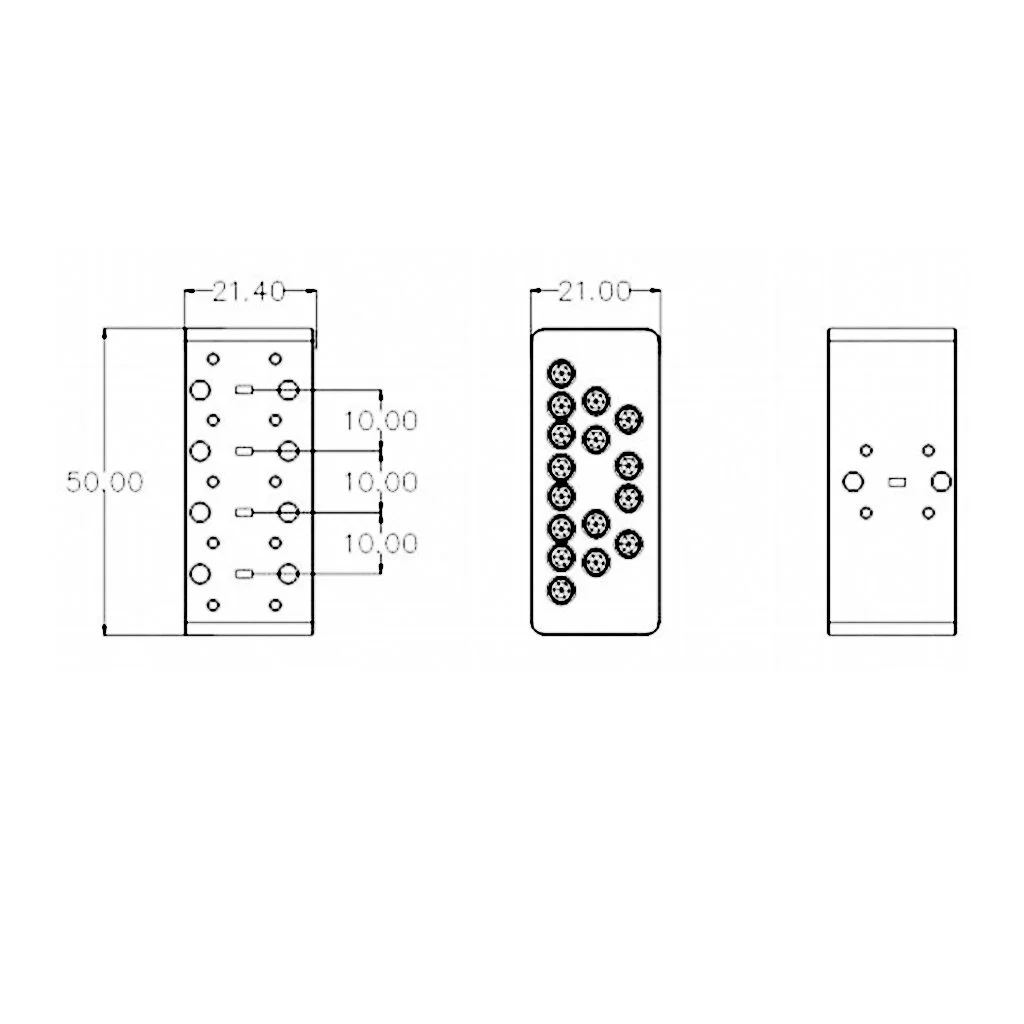
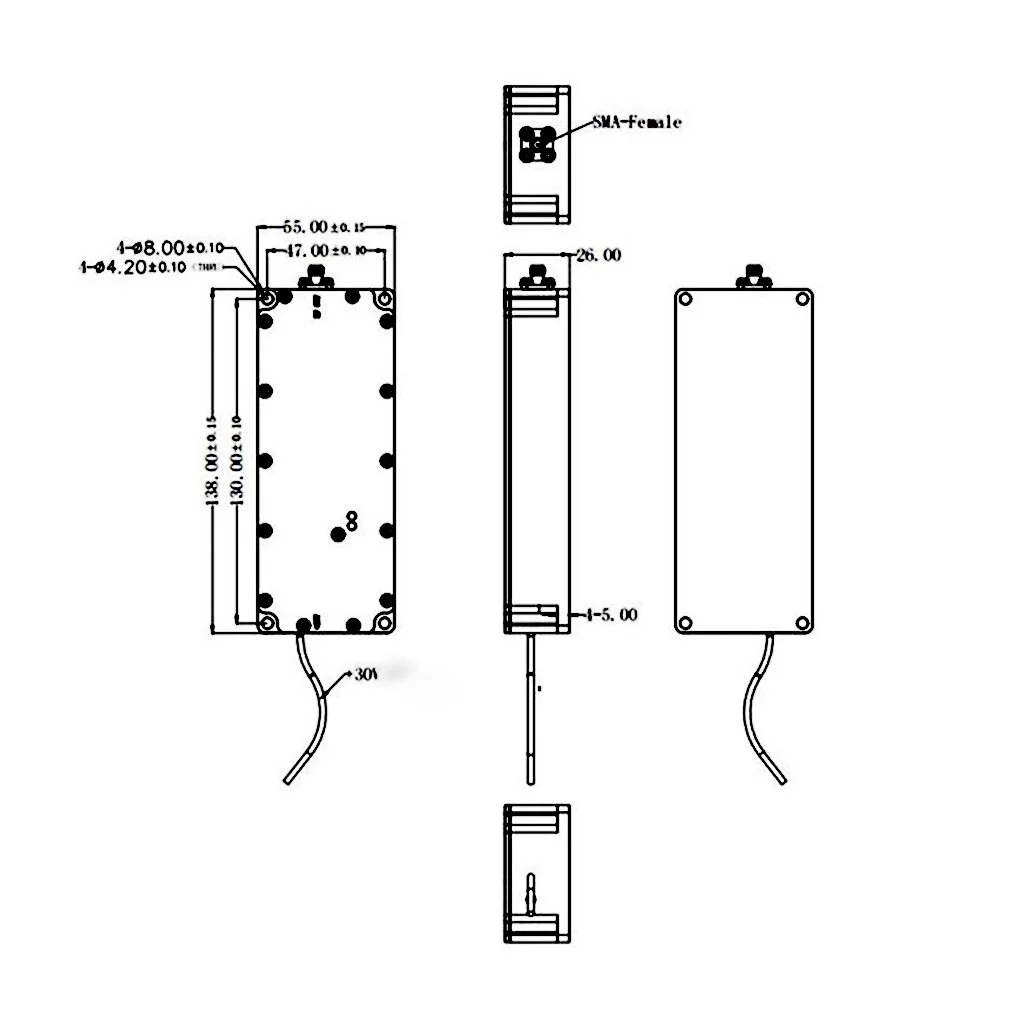
Ku Frequency Band LNB
A Ku frequency band LNB (Low-Noise Block downconverter) is a specialized device used in satellite communication systems to receive signals within the Ku band spectrum, typically ranging from 12 to 18 GHz. This frequency band is popular for direct broadcast satellite services, including satellite TV, VSAT, and broadband internet, due to its ability to offer higher bandwidth and improved signal quality compared to lower frequency bands.
The Ku band LNB works by capturing high-frequency satellite signals through a dish antenna and converting them into lower frequencies (usually in the L-band) that can be readily processed by satellite receivers. Key features of Ku band LNBs include low noise figure for minimal signal degradation, high gain to amplify weak signals, and resistance to weather interference, making them ideal for both residential and professional applications.
Innovations in Ku band LNB technology focus on enhanced signal stability, multi-band capability, and compatibility with modern digital modulation standards, ensuring reliable, high-quality reception in diverse environments. Their compact design and efficient performance make Ku frequency band LNBs a cornerstone component in the evolving landscape of satellite communications.